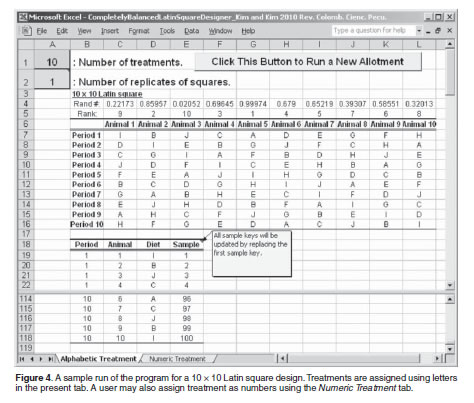
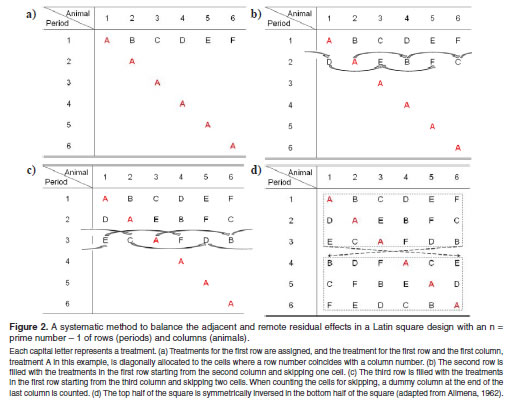
The systemic method balances the residual effects when a treatment is an even number. A systemic method for balanced Latin square designs. Balanced latin square design.
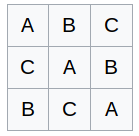
Balanced Latin Square Design, One common way to assign treatments to subjects is to use a Latin square design. An advantage of this design for a repeated measures experiment is that it ensures a balanced fraction of a complete factorial that is all treatment combinations represented when subjects are limited and the sequence effect of treatment can be considered to be negligible. -The most common sizes of LS are 5x5 to 8x8 Advantages of the LS Design 1. For some experiments the size of blocks may be less than the number of treatments.
 Within Subject Study Designs Latin Square Paasp Network From paasp.net
Within Subject Study Designs Latin Square Paasp Network From paasp.net
A systemic method for balanced Latin square designs The systemic method balances the residual effects when a treatment is an even number. In this example treatments A to F are ordinarily assigned in the first row animal. 3112 Latin Square Example Peanut Varieties Example. Refers to a single Latin square with an even number of treatments or a pair of Latin squares with an odd number of treatments.
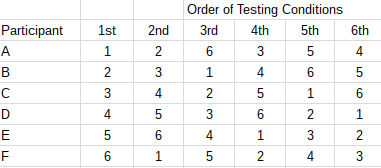
There are six Williams squares possible in case of four treatments.
Read another article:
There are other variations of counterbalanced measures designs. For example in the above 3 x 3 example square treatment B follows A three times in the rows. Three treatment groups A B C three periods period 1 period 2 and period 3 and six sequences ABC BCA CAB CBA ACB and BAC. It follows C zero times. For some experiments the size of blocks may be less than the number of treatments.
 Source: scielo.org.co
Source: scielo.org.co
-The most common sizes of LS are 5x5 to 8x8 Advantages of the LS Design 1. A design can be developed from a set of n-l mutually orthogonal Latin squares obeying certain restrictions. One common way to assign treatments to subjects is to use a Latin square design. Latin Square Design 21 Latin square design A Latin square design is a method of placing treatments so that they appear in a balanced fashion within a square block or field. A Program For Making Completely Balanced Latin Square Designs Employing A Systemic Method.
 Source: scielo.org.co
Source: scielo.org.co
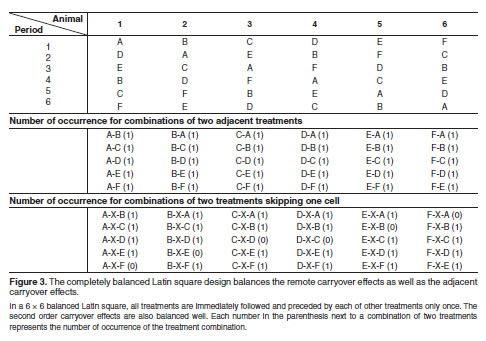
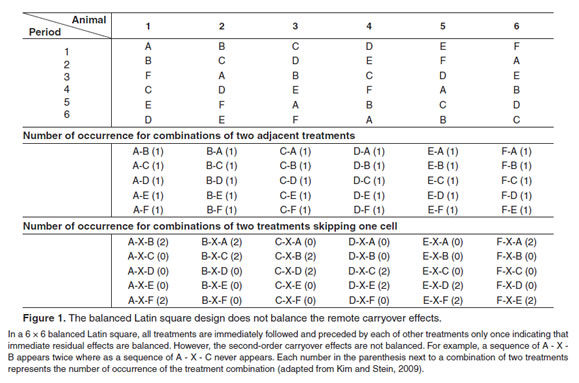
In a 6 6 balanced Latin square all treatments are immediately. For example in the above 3 x 3 example square treatment B follows A three times in the rows. The systemic method balances the residual effects when a treatment is an even number. A plant biologist conducted an experiment to compare the yields of 4 varieties of peanuts A B C D. A Program For Making Completely Balanced Latin Square Designs Employing A Systemic Method.
 Source: yorku.ca
Source: yorku.ca
Because the designs are balanced all treatment di erences have the same estimated variance. If the number of treatments to be tested is even the design is a latin square otherwise it consists of two latin. Carryover balance is achieved with very few subjects. Constructing the Williams squares is not a randomization yet. Within Subjects Vs Between Subjects Designs Which To Use.
 Source: scielo.org.co
Source: scielo.org.co
BALANCED LATIN SQUARE. Treatments appear once in each row and column. Latin square designs and the related Graeco-Latin square and Hyper-Graeco-Latin square designs are a special type of comparative design. A systemic method for balanced Latin square designs The systemic method balances the residual effects when a treatment is an even number. A Program For Making Completely Balanced Latin Square Designs Employing A Systemic Method.
 Source: paasp.net
Source: paasp.net
There are six Williams squares possible in case of four treatments. The systemic method balances the residual effects when a treatment is an even number. Williams row-column designs are used if each of the treatments in the study is given to each of the subjects. Thus if there are more than four subjects more than one Williams square would be applied eg. Within Subject Study Designs Latin Square Paasp Network.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
The balanced design is invented in order toaccount for first order carry-over effects eg. Treatments are assigned at random within rows and columns with each treatment. 3112 Latin Square Example Peanut Varieties Example. The systemic method balances the residual effects when a treatment is an even number. Natural Phenomena Integrates The Physical And Social Conditions That Frame The Project The Form And Special Arrangement Natural Phenomena New Museum Physics.
 Source: scielo.org.co
Source: scielo.org.co
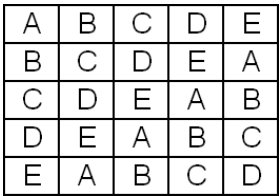
Since not all the treatments can be compared within each block a new class of designs called balanced incomplete Latin squares BILS is proposed. A Latin square is a block design with the arrangement of v Latin letters into a vv array a table with v rows and v columns. Treatments appear once in each row and column. -The most common sizes of LS are 5x5 to 8x8 Advantages of the LS Design 1. A Program For Making Completely Balanced Latin Square Designs Employing A Systemic Method.
 Source: statisticshowto.com
Source: statisticshowto.com
Constructing the Williams squares is not a randomization yet. Latin square and related designs are efficient designs to block from 2 to 4 nuisance factors. -Treatments are arranged in rows and columns -Each row contains every treatment. I thead_innerHTML i 1. Latin Square Design Definition And Balanced Latin Square Algorithm Statistics How To.
 Source: statisticshowto.com
Source: statisticshowto.com
It follows C zero times. Treatment peanut variety Column. Latin square designs allow for two blocking factors. -Each column contains every treatment. Latin Square Design Definition And Balanced Latin Square Algorithm Statistics How To.
 Source: dictionary.apa.org
Source: dictionary.apa.org
While a Latin square ensures that each letter appears an equal number of times it doesnt protect against order effects. The systemic method balances the residual effects when a treatment is an even number. Because the designs are balanced all treatment di erences have the same estimated variance. Since not all the treatments can be compared within each block a new class of designs called balanced incomplete Latin squares BILS is proposed. Balanced Latin Square Apa Dictionary Of Psychology.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
A plot of land was divided into 16 subplots 4 rows and 4 columns The following latin square design was run. Treatments appear once in each row and column. In this example treatments A to F are ordinarily assigned in the Þ rst row animal. A systemic method for balanced Latin square designs The systemic method balances the residual effects when a treatment is an even number. New Balance Logo Logok New Balance Logo Corporate Id.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
A plot of land was divided into 16 subplots 4 rows and 4 columns The following latin square design was run. Since not all the treatments can be compared within each block a new class of designs called balanced incomplete Latin squares BILS is proposed. There are other variations of counterbalanced measures designs. Treatments for the Þ rst column. Rainbow Squares Black By Lorna Hooper Rainbow Rainbow Wallpaper Square Wall Art.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
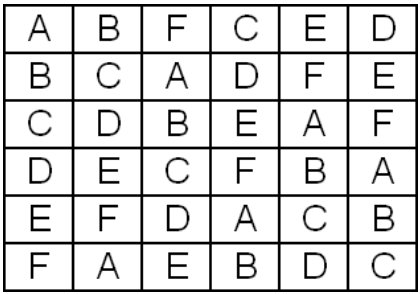
A balanced 6 6 Latin square design using this method is illustrated in Figure 2. The responses are given in the table to the right. -The most common sizes of LS are 5x5 to 8x8 Advantages of the LS Design 1. With the Latin Square listed below we can easily construct the crossover design with treatments periods and sequences. Medieval Dietetics The Theory Of Humours 4 Temperaments Greek Medicine Medical Knowledge Humor.
 Source: statisticshowto.com
Source: statisticshowto.com
In balanced square lattice designs r k1 or t k2 implying 1. A balanced 6 6 Latin square design using this method is illustrated in Figure 2. In this example treatments A to F are ordinarily assigned in the first row animal. In this example treatments A to F are ordinarily assigned in the Þ rst row animal. Latin Square Design Definition And Balanced Latin Square Algorithm Statistics How To.
 Source: yorku.ca
Source: yorku.ca
-Each column contains every treatment. If the number of treatments to be tested is even the design is a latin square otherwise it consists of two latin. There is a single factor of primary interest typically called the treatment factor and several nuisance factors. The balanced design is invented in order toaccount for first order carry-over effects eg. Within Subjects Vs Between Subjects Designs Which To Use.







